node虽然是单进程单线程运行的,但是也提供创建子进程让程序运行的更加快速,稳健。创建方法如下:
spawn: 用法:spawn(command[, args][, options]),具体的参数请看官网。
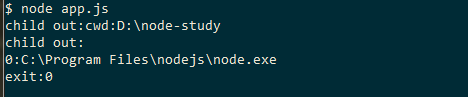
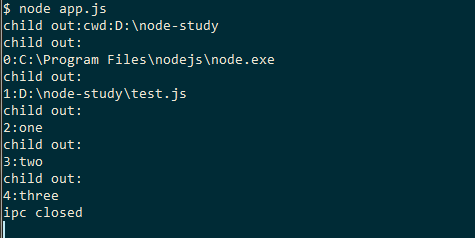
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 // app.js'child_process' );'node' , ['test.js' , 'one' , 'two' ,'three' ],{stdio:['pipe' ,'ipc' , 'ignore' ]});'node' ,['test1.js' ],{stdio:['pipe' ]});'message' , function (data){'child out:' +data);'exit' ,function (code, signal){'exit:' +code);exit ();'error' , function (err){'error:' +err);exit ();'disconnect' ,function (){'ipc closed' );
1 2 3 4 5 // test.js'cwd:' + process.cwd());forEach (function (val, index ){'\r\n' +index +':' +val);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 // test1.js'fs' );'./space.txt' );'data' ,function (data){'end' ,function (){exit ();
这时直接运行:
发现test.js 中的data还没发送完成到父进程,程序就exit 了,查看官网exit事件,有一句解释 当 ‘exit’ 事件被触发时,子进程的 stdio 流可能依然是打开的 。也就是说,子进程一旦结束就触发exit事件,但是数据有可能还没传输完成,这样就解释的通了,
这样就运行正确了。
fork: 用法:fork(modulePath[, args][, options])[options]silent: false继承父进程的stdio,设置为true,子进程的stdin、stdout和stderr都会通过管道传递到父进程,否则他们将会从父进程继承。[options]stdio:[0,1,2,’ipc’], 如果要设置该属性值,则必须有个值为‘ipc’,否则报错。
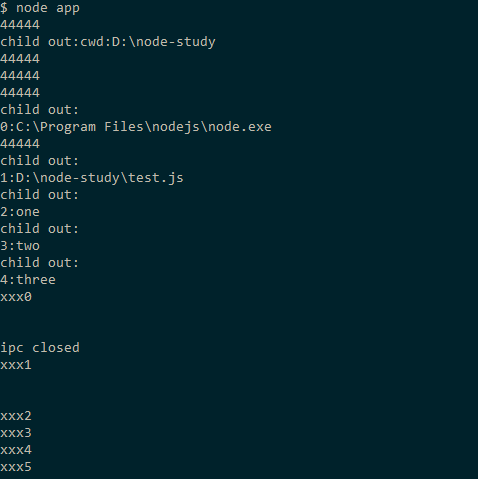
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 const { fork } = require ('child_process' );var sp1 = fork('test.js' , ['one' , 'two' ,'three' ]);var sp2 = fork('test1.js' ,{silent : true });'message' , function (data )console .log('child out:' +data);'data' ,function (data )console .log(data.toString() + '\r\n' );'error' , function (err )console .log('error:' +err);'disconnect' ,function (console .log('ipc closed' );
1 2 3 4 5 6 // test.js'cwd:' + process.cwd());forEach (function (val, index ){'44444' );'\r\n' +index +':' +val);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 var fs = require ('fs' );var out = fs.createWriteStream('./space.txt' );var i = 0 ;on ('message' ,function(data ){log ('xxx' + i);data );
运行结果如下:
可以看到silent:false时,和父进程共享stdio,silent为true时,子进程的stdio事件被传递到父进程上,通过监听stdio上的data事件可获取子进程中的输出数据。输出的结果杂乱无序,可以看出多进程是各自运行的。
exec: 用法:exec(command[, options][, callback])exec通过命令生成一个shell来运行相关的子进程。和spawn的区别是exec子进程返回的stdio数据是同步的,而spawn是异步的。
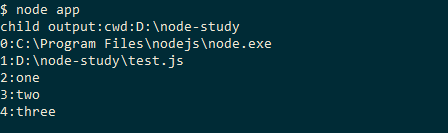
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 // app.js'child_process' );'node test.js one two three' ,function (err, stdout, stderr){if (err) {'error:' + err);exit ();else {'child output:' +stdout.toString());'node test1.js' ,function (err, stdout, stderr){exit ();
1 2 3 4 5 // test.jsstdout .write ('cwd:' + process.cwd());function (val, index) stdout .write ('\r\n' +index+':' +val);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 // test1.js'fs' );'./space.txt' );'data' ,function (data){exit ();
运行结果:
execFile: 用法:execFile(file[, args][, options][, callback])
翻看源码exec是对execFile的封装,而execFile和fork底层都是调用的spawn。
cluster: node提供cluster模块充分利用多核cpu对子进程处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 var cluster = require ('cluster' );var http = require ('http' );const numCPUs = require ('os' ).cpus().length;if (cluster.isMaster){for (var i = 0 ; i < numCPUs; i++) { console .log('run in main process' );else {function (req, res )if (req.url !== '/favicon.ico' ) {200 , {'Content-Type' : 'text/html' });'<head><meta charset="utf-8"/></head>' );'hello\n' );console .log('run in child process' );1337 );
运行node app, 先输出 run in main process, 然后打开浏览器localhost:1337,则会发现输出 run in child process.
对于操作系统中其实是不允许多个进程对同一个端口进行监听的,cluster生成子进程其实是利用的child_process.fork(),实现的原理其实是 利用主进程process.send方法中的第二个参数process.send(message [, sendHandle])将服务器对象或者socket对象传输给子进程,从而创建的子进程们都监听同一个socket端口对象。